|
|
|
Research Activities
Background and Aims
Our long-term goal is to understand the molecular mechanisms defining morphogenetic
interactions of cells with their surrounding microenvironment, i.e., extracellular
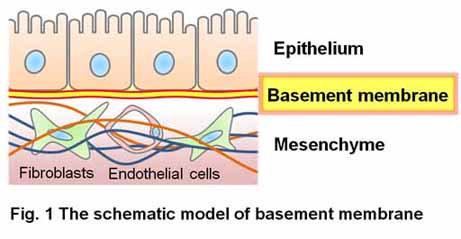
matrices. We are particularly interested in the roles of the basement membrane
(Fig. 1) in histogenesis/organogenesis, with and emphasis on the molecular interactions
of basement membrane proteins with their receptors on the cell surface
as well as the resulting signaling events that regulate proliferation,
differentiation, apoptosis, and motility of cells. Emphasis is also gevin
to the fabrication of culature substrates customized for individual cell
types including pluripotent and tiwwue stem cells to promote stem cell
research and regenerative medicine.
Our current research efforts are focused on the following topics:
1) Comprehensive immunohistochemical localization of basement membrane
proteins in mouse embryos
2) Structure-function relationships of laminins and integrins
3) Designer laminin fragments for regenerative medicine and stem cell research
4) Physiological functions of polydom, a mesenchymal protein, in lymphangiogenesis
1) Comprehensive immunohistochemical localization of basement membrane proteins in mouse embryos
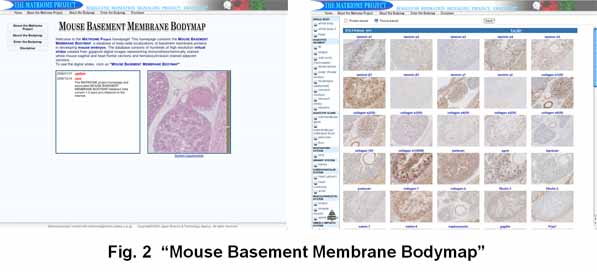
We have constructed a body map of basement membrane proteins, which reperesents
the comprehensive immunohistochemistry-based expression profiles of the
tissue-specific customization of basement membranes in mice.
The resulting immunohistochemical data have been compiled into a hugh resolution
image database "Mouse Basement Membrane Bodymap" (Fig. 2).
http://dbarchive. biosciencedbc.jp/archive/matrixome/bm/home.html
(Manabe et al., PNAS, 2008)
2) Structure-function relationships of laminins and integrins
"Laminin", a major compotent of basement membrane, interacts with cell sufrace receptor "integrin", and regulates various cell behaviour (Fig. 3).
To understand the physiological functions of laminin-integrin interaction,
we employed various approaches at different levels, i.e. from the molecular
level (crystallization; Fig. 4, biochemistry) to the whole-body level (knockout/knock-in mice model).
(Nishiuchi et al., Matrix Biol., 2006; Ido et al., JBC, 2007; Taniguchi et al., JBC, 2009; Takizawa et al., Sci. Advances, 2017)
3) Designer laminin fragments for regenerative medicine and stem cell research
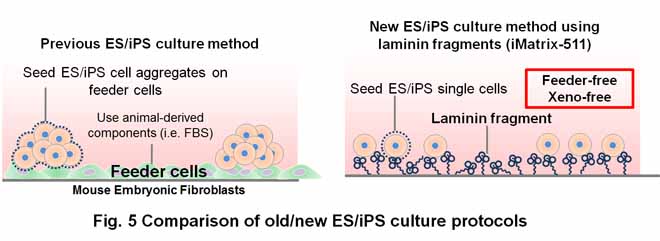
In collaboration with Institute for Frontier Medical Sciences and Center for iPS cell Research of Kyoto University, we demonstrated that laminin-511 (alpha5beta1gamma1) and its fragment (Fig. 3) support rebust propagation of human ES/iPS cells in an undifferentiated
state in cultures using defined and xeno-free media combined with single cell passaging (Fig. 5).
The laminin-511 fragment has now been commercially available under the
trade name of "iMatrix-511", which is suitable for production
of clinical-grade human ES/iPS cells and other stem cells in regenerative
medicine.
(Miyazaki et al., Nat. Commun., 2012; Nakagawa et al., Sci. Rep., 2014; Doi et al., Stem Cell Rep., 2014)
4) Physiological functions of polydom, a mesenchymal protein, in lymphangiogenesis
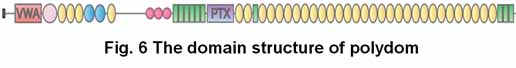
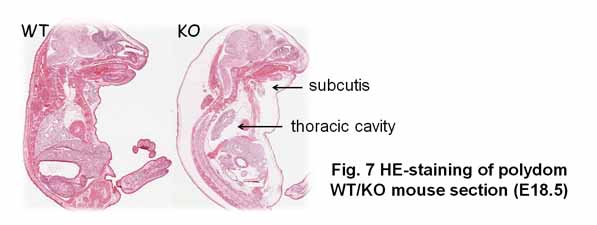
"Polydom" is a newly identified extracellular matrix protein that binds to integrin alpha9beta1 with high affinity (Fig. 6). (Sato-Nishiuchi et al., JBC, 2012)
To adress the physiological roles of polydom, we generated polydom-deficient
mice. The polydom-deficient mice showed severe edema and dies immediately
after birth due to the defects in lymphatic vessel development (Fig. 7). (Morooka et al., Circulation Res., 2017)
Currently, we are focusing on the mechanistic basis of the lymphatic phenotype
of polydom-deficient mice.
The major achievements in our laboratory during the past few years are
listed in Publication List.
|
|
|
|
 |
|